
In recent years, virtual private server (VPS) hosting has been a sweet spot between the affordability of shared hosting and the power of a dedicated server. The introduction of cloud infrastructures has taken that concept and extended it even further. The possible uses for Linux VPS Hosting are almost endless.
When you run a business, you can’t risk having a subpar website. It takes high availability (HA) 24/7 to meet the demands of your customers and users. If your website has been operating on a shared server and you’ve noticed some performance issues, particularly due to high database usage, it might be time to consider migrating to a high availability VPS.
Imagine what would happen if a customer visits your eCommerce store and he can’t complete the checkout process because it’s running too slow. Worse yet, what if nothing loads—there’s just a blank screen because your site is down. The customer moves on to your competitor.
Many small-to-midsize businesses (SMBs) that start out on a shared server eventually notice problems like those mentioned above. If your website drives a lot of revenue for your company, even a small amount of downtime can put a big dent in your bottom line and return on investment (ROI).
This drives business owners toward VPS hosting.
Traditional — not high availability — VPS hosting was once thought of as a stepping stone between a basic shared server and your own dedicated equipment. It’s still shared with other users on the same physical server, but you’re allocated a dedicated percentage of computing resources. With a traditional VPS you’re much less affected by your neighbors’ usage of bandwidth and other resources.
The problem is that there is still a risk of downtime. Those unbreached server resources mitigate some risk. However, there’s still residual risk because if that single physical server goes down, so will your website. It’s a single point of failure.
This is what makes high availability VPS different from traditional VPS.
- What is High Availability?
- What Are The Benefits of High Availability VPS?
- High Availability with Server Monitoring
- Server Snapshot Rollbacks
- How Do I Know If High Availability VPS Is for Me?
What is High Availability?
In computing, the term availability refers to the uptime and reliability of the service or system that you’re using. Availability is often measured in terms of percentages. Typically within the hosting industry, you will see 99.999% uptime (approximately five minutes of downtime annually) as the measurement meaning that 100% is no downtime whatsoever. This is typically achieved with a few components working together.
- Server clusters have data cloned across multiple nodes for redundancy, similar to redundant array of independent disks (RAID). If a VPS instance on the main node fails, it spins up on the next available node.
- Load balancers, software or hardware, using algorithms such as round robin domain name system (DNS) and server response time to determine the fastest and most reliable node to handle a request at that time.
- An advanced network configuration accommodates multiple load balancers communicating uptime stats with each other to further mitigate the dangers that come with both hardware failure and software issues.
In summary, a high availability strategy involves replicated server nodes so that if the primary VPS fails, a duplicate node takes over. This is how high availability VPS hosting reduces costly downtime.
High Availability vs Fault Tolerance
Fault tolerance is similar to high availability except while a highly available environment seeks minimal downtime, a fault tolerant infrastructure has achieved no minimal interruption. You will often hear of fault tolerant systems compared to a twin-engine airplane. If one engine goes out, the other engine takes over and allows the plane to keep flying. In a highly available system there may be downtime, but services come back online quickly.
Why choose a high availability system instead of fault tolerant system? In general, high availability is much more affordable than fault tolerance, for websites and resources that could tolerate minimal downtime.
How Is High Availability Calculated?
Or, how do we arrive at the five nines? There are many different ways of calculating availability, but generally, the formula involves dividing uptime by uptime plus downtime and then multiplying that by a hundred to get a percent value. It may seem pretty simple, but a lot of painstaking effort goes into creating this kind of availability.
What Are The Benefits of High Availability VPS?
Value per cost. Customers have constant access to server-based resources. High availability solutions come in significantly cheaper than fault tolerant systems for online businesses that can handle an intermittent outage.
Redundancy. A high availability system safeguards data by storing it in multiple locations. The failure of a single VPS doesn’t automatically result in devastating loss.
Disaster recovery. Any unexpected downtime is reduced to improve service level agreement (SLA) items including lower recovery point objective (RPO) and recovery time objective (RTO).
High Availability with Server Monitoring
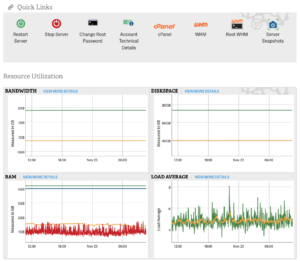
For improved transparency with high availability, all InMotion VPS and dedicated server hosting plans include server monitoring in the Account Management Panel (AMP) Manage My Cloud Server section for tracking resource utilization.
At the top you’ll find quick links to easily:
- Restart and stop your server
- Change your root password
- View hosting account technical details
- Access cPanel and WebHost Manager (WHM)
Under the quick links are the resource utilization monitors for your server’s bandwidth, and disk space, RAM, and CPU load average within the last 24 hours. Hover your cursor over the chart for specs into the thousandths range.
Bandwidth
The bandwidth graph displays two lines. The green line represents the bandwidth input and the yellow line the bandwidth output on the server in gigabytes (GB). Bandwidth is affected by processes including website traffic, sending/receiving emails, and database queries.
You can improve web bandwidth by integrating your server with the Cloudflare content delivery network (CDN).
Disk Space
The disk space graph displays two lines. The green line indicates total disk space determined by your hosting package and the yellow line your used disk space in GB.
Removing older backups is a quick way to restore server disk space.
Random Access Memory (RAM)
The RAM graph displays four lines measured in GBs. The green line shows total memory for your server. The yellow line shows cached memory on the server. This is the best indicator of how much RAM you’re actually using. The red line is free memory. And the blue line is your hosting plan’s limit.
Load Average
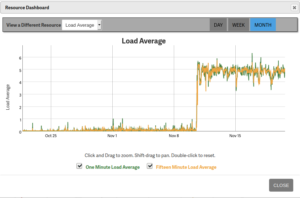
The green and yellow load average lines indicate your one minute and fifteen minute load average respectively. Your baseline load average may increase as you install more web applications. It may also spike as more internal tasks such as backups and updates are run simultaneously. Neither of these cases are negative if the server infrastructure is configured to handle it.
Audit this graph regularly to better understand your baseline load average. Or for more in-depth system reporting, install security information and event management (SIEM) software – e.g. Splunk or Elastic (ELK) Stack.
Server Snapshot Rollbacks
Server snapshots aid disaster recovery efforts by allowing you to instantly revert to a previous stable system of files and processes with only a few clicks. A snapshot differs from traditional backup created with tar or zip compression tools in that you cannot restore individual files from a snapshot. While we recommend having regular compressed backups to restore individual files when needed, snapshots are a valuable last line of defense.
Data rollback, backups, and snapshots are just as important to the high availability infrastructure as the server and network components.
Common use cases for snapshot rollbacks:
- Application upgrades (most common) – Imagine upgrading to the latest version of WordPress and your site fails to function correctly afterward. You can easily revert back to the working version of your site within minutes instead of searching for an old MySQL database backup to restore. That’s assuming you have a recent backup.
- Security issues – If your site gets hacked, you may be able to revert to an older, uninfected snapshot instead of cleaning up the cyber attack. Sometimes, you have to learn about cybersecurity the hard way. This makes it easier.
- Development bugs – A developer in a staging environment preparing to roll out some new code can easily revert back to a stable version if the new commits cause other bugs around the site.
These are just some of the scenarios you may face where the new snapshot feature may come in handy on a self-serve basis.
How Do I Know If High Availability VPS Is for Me?
Time is money—and downtime is money lost. If you have resources that need to be up constantly, like an HA application, then you need a highly available system.
This is particularly true in today’s world, where 81% of consumers head online before making a purchasing decision. It doesn’t matter what industry you’re in; consumers will look at your website.
If your website is down, slow, or doesn’t function properly, your audience will leave. If that’s something you’re concerned about, it may be time to check out high availability VPS. Learn how we can help you make the best first impression possible with our high availability VPS Hosting. At InMotion Hosting, we know how to do HA right.
Nice article! Thanks for sharing this informative post. Keep posting!