
Search intent can tell you a lot about what internet users are looking for and why they are looking for it.
In this article, we will explain what search intent is, cover the different types of search intent, and tell you how you can optimize your content for search intent to help drive traffic.
- What is Search Intent?
- Why Search Intent Matters for SEO
- Types of Search Intent
- How to Optimize for Search Intent
What is Search Intent?
When someone searches the internet for something, they have a goal in mind they are trying to accomplish.
Search intent (also known as user intent or audience intent) is the purpose of a user’s search query. It is the “why” behind a search query and the main goal a user has in mind when they perform a search.
Google automatically interprets search intent and shows users the search results that align with that intent.
As a marketer, search intent can tell you a lot about where that user is in the conversion funnel. If you can determine search intent, then you can create content that effectively targets potential clients.
Why Search Intent Matters for SEO
The main reason search intent matters is that is important for SEO. Your ability to understand search intent can have a large impact on your page rankings and whether or not readers think your page met their needs.
Users want results that provide the information they are looking for.
Can you imagine searching for the history of cars but only seeing search results attempting to sell you a new car instead? You would likely find that very frustrating. When you understand search intent, you provide a better overall experience for your readers.
SEO Benefits of Intent Targeting
Helping your readers is always a good call, but how does that help your SEO?
If you can accurately understand search intent, it can benefit your SEO in several ways including:
- Increased page views: When you accurately understand a user’s search intent and give them the information they were searching for they are more likely to engage with other areas of your website.
- Reduced bounce rates: When users find what they want on your page the better their chances of staying on that page are.
- Better chance at landing featured snippets: Featured snippets are excellent for SEO because they land your content above even the top-ranked search result.
- Wider audience reach: Not everyone searches the same, but thankfully Google is smart enough to interpret different queries that are related to match them with the same topic and intent. If you successfully answer a question, Google is more likely to use that for other related queries.
Types of Search Intent
Search intent can be broken down into four main types:
- Informational: The user is trying to learn more about a subject (example: what is a good gaming system? )
- Navigational: The user is trying to find something (example: PlayStation website )
- Transactional: The user wants to complete a specific action (example: buy PlayStation 5)
- Commercial: The user is comparing options or wants to learn more before making a purchase (example: PlayStation 5 vs Xbox Series X)
Below we will cover the four different types of search intent in detail and explain how they relate to specific stages of the customer journey.
Informational Search Intent
Users with informational search intent are those who are searching for information on a given topic or looking for an answer to a specific question. They want to learn something.
A lot of times these queries are in the form of questions and use interrogative words such as who, what, where, when, why, and how.
An example of an informational search could be someone searching for “how to cook pasta?”
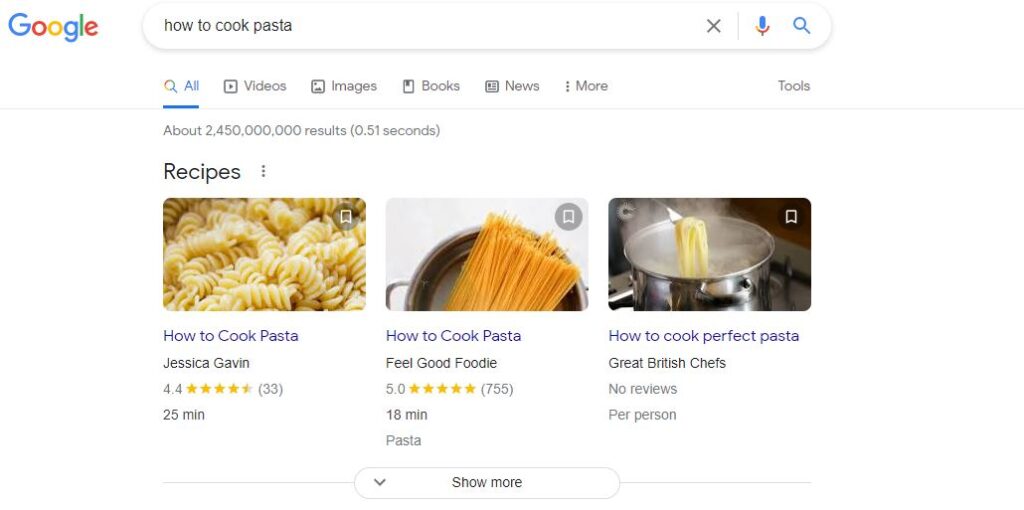
A majority of search queries performed on Google are informational searches, which means creating informational or educational content for your audience can be a good way to increase your visibility while simultaneously building trust in your expertise on a given subject.
Navigational Search Intent
With navigational search intent, the user performing the search is looking to visit a specific website, page, or domain. These are users who already know what they are trying to find.
For these types of searches, it is usually quicker for the searcher to type where they want to go into Goole rather than fill out the entire URL in the browser’s address bar.
A common example of navigational search intent is someone searching for “Facebook login.”
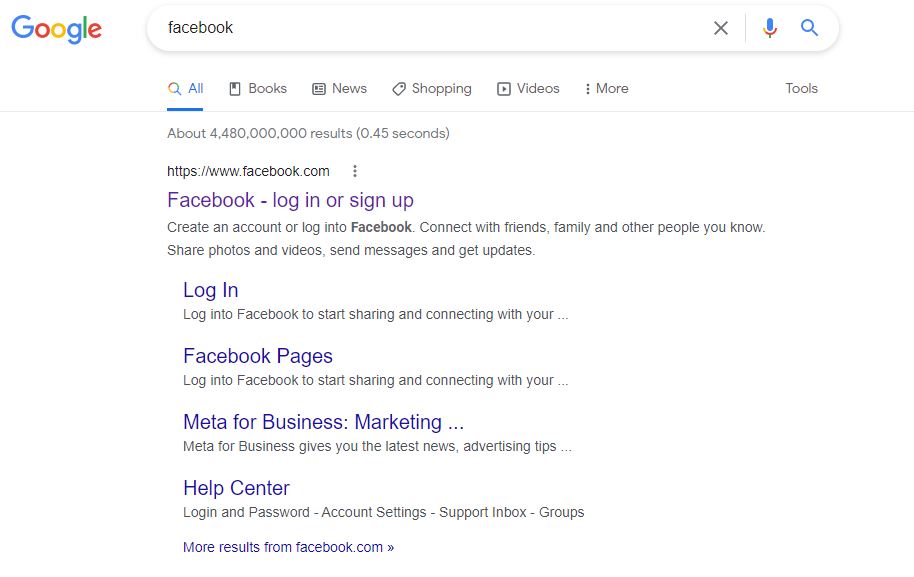
However, Google doesn’t need the word “login” to know where you want to go. Chances are if you just type “Facebook” into your search bar Google will recognize it as a navigational search and assume you are looking for Facebook’s homepage.
Transactional Search Intent
Users with transactional search intent are those who are ready to make a purchase at the time of their search. These users typically know exactly what they want and want to get to that product or company page immediately.
At this point of the customer journey, users are done researching a product and are now looking for a place to purchase it.
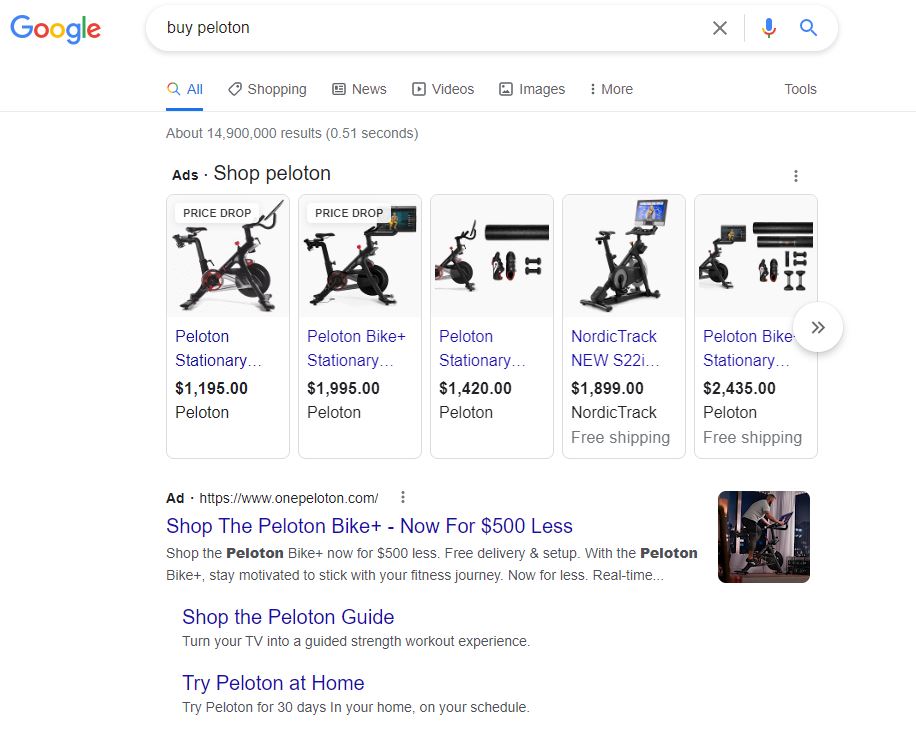
Using “buy peloton” as an example, here is what we see:
Commercial Search Intent
Commercial search intent (also known as commercial investigation) applies to users who likely want to make a purchase soon, but are still comparing their options.
It is almost like a mix of informational and transactional search intent because these users have transactional intent but they still want to learn more before completing a purchase.
At this point, customers are typically comparing brands and products to find the best solution for their needs.
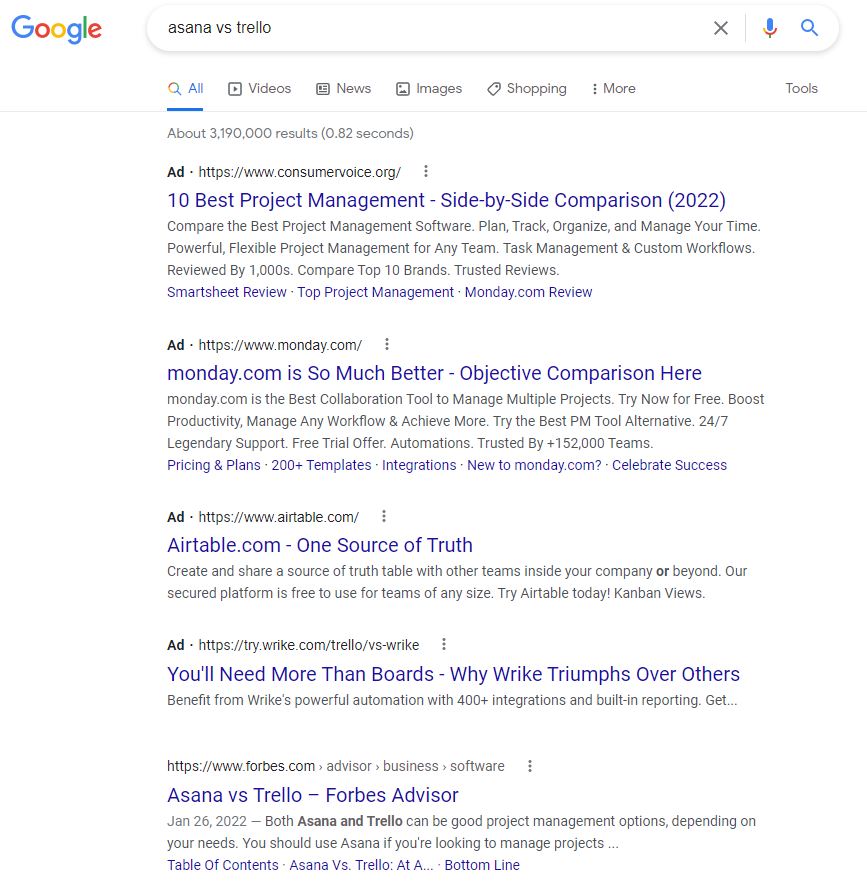
If you were looking into project management solutions, you might search for “Asana vs Trello,” and this is what you would see:
How to Optimize for Search Intent
Keyword Intent
The keywords used in a search query can often tell you a lot about a user’s search intent.
The keywords themselves are helpful, but so are the modifiers used with those keywords.
Let’s look at some words you are likely to see with different types of search intent:
- Informational: who, what, where, when, how to, why, information, guide, tutorial, examples
- Navigational: login, customer service, [product name], [service name], [brand name]
- Transactional: purchase, buy, order, coupon, price, deal, sale
- Commercial: comparison, vs, alternatives, review, best
Match Metadata with Intent
It is important to use valuable keywords in your content, and those same keywords can help optimize your content’s metadata for SEO.
Your content should also apply whatever keyword you are targeting to that article’s title tag and headings.
If you have good, accurate metadata that includes your target keywords it can help your click-through rate (CTR).
Look at Your Competition
It’s always a good idea to do some competitor analysis, and that’s an easy place to start when optimizing for search intent.
You already know who your top competitors are and who the leaders are when it comes to your industry. Take some time looking at the top-ranking pages for the topics or products you would like to rank for and notice how they are crafted. These pages are ranking high for a good reason.
Study the high ranking SERPs and things to pay attention to things like:
- Format
- Tone
- Information covered
- What information is not included
Determining search intent is an effective way to improve your overall SEO.
Want more SEO tips? Check out SEO For Beginners – A Comprehensive Guide.

Comments
It looks like this article doesn't have any comments yet - you can be the first. If you have any comments or questions, start the conversation!