In this Article:
- How are passwords cracked?
- Password entropy and understanding password strength
- Creating stronger passwords with higher entropy
- Dictionary attacks complicate matters
- Create a strong password you can remember
- Generate a random strong password in cPanel
These days on the Internet all of your important information could be just a website request away. This is why it’s important as ever to ensure that you’re using a secure password to restrict access to your private information.
You should keep your AMP, cPanel, and Email passwords secure, as well as any CMS such as WordPress. Anything that’s publicly accessible on the Internet should be using a strong password for your security.
It’s typically better to come up with a secure password that you can actually remember, otherwise you’ll probably rely on writing it down or storing it on your computer which could potentially be hacked.
Looking on the web about password strength, chances are you’ll run across the xkcd: Password Strength comic.
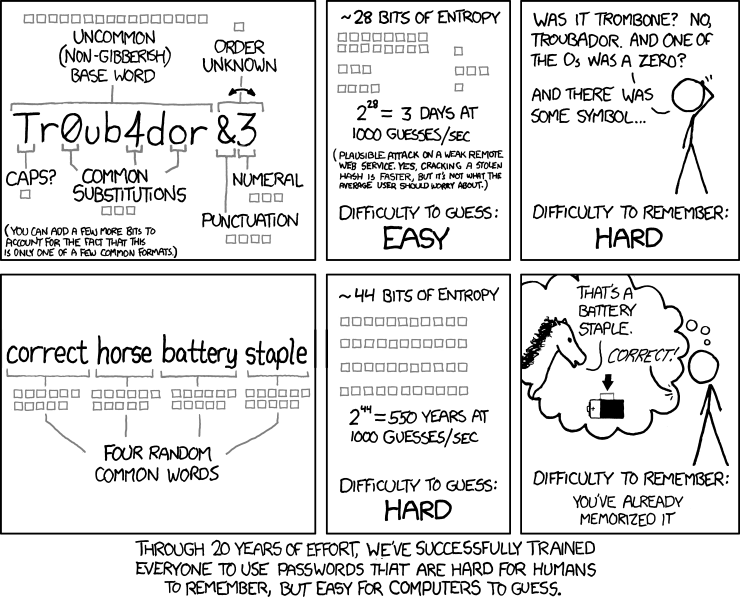
How are passwords cracked?
Most accounts that have their passwords compromised are not done so by another human being directly.
Instead a computer will be tasked with guessing your password, so planning should go in to understanding and then deterring a computer from cracking your password.
A hacker has a variety of malicious tactics available to them when trying to crack your password. These would be the two most common attacks you see on the Internet today:
| How it works | How to prevent | |
|---|---|---|
| Brute Force Attack | The attacker runs a script that tries again and again to randomly crack your password by sheer brute force. | A long password with multiple character sets is the best protection. The higher your password entropy the less likely your password will be compromised by a brute force attack. |
| Dictionary Attack | The attacker utilizes dictionaries of known words or passwords and a script to try them in thousands of combinations until one matches up with the correct password. | Don’t use common words, or keystrokes such as qwerty or 123456. Use a combination of multiple character sets to reduce the likelihood of multiple entries pulled for a dictionary matching up successfully. |
Password entropy and understanding password strength
In the world of computing and passwords, there is something commonly referred to as password entropy.
define entropy: lack of order or predictability; gradual decline into disorder.
In layman’s terms this basically means the higher your password entropy the less predictable your password patterns are for a computer, so the stronger and more secure your password is theoretically.
This is a simple equation to demonstrate password entropy:
H total binary bits of entropy | L length of your password | N number of possible symbols in password
H = L * log2(N)
Depending on how the password was generated, either by a random sequence or a human, this equation can get a lot more complex. But for our purposes here it should work fine.
Creating stronger passwords with higher entropy
Knowing how entropy is calculated, we can see that doing certain things to our password adds more than others.
The length of your password can add a lot of entropy to your password, but adding complexity by using more than one character set can also greatly increase it.
This is why typically most sites require you to use at least one uppercase, one lowercase, one digit, and one special symbol character in your password.
Your typical online account password can be made up of a possible 94 characters in each character slot.
| 26 lowercase letters | abcdefghijklmnopqrstuvwxyz |
|---|---|
| 26 uppercase letters | ABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRSTUVWXYZ |
| 32 special characters | `[email protected]#$%^&*()-_=+[]{}|;:'”,<.>/? |
| 10 numbers | 0123456789 |
Using digits only 0-9
Using lowercase letters only
| Characters | Equation | Bits | Passwords |
|---|---|---|---|
| 5 | 5 * log2(10) | 16.6096 | 100,000 |
| 6 | 6 * log2(10) | 19.9315 | 1 Million |
| 7 | 7 * log2(10) | 23.2534 | 10 Million |
| 8 | 8 * log2(10) | 26.5754 | 100 Million |
| 12 | 12 * log2(10) | 39.8631 | 1 Trillion |
| Characters | Equation | Bits | Passwords |
|---|---|---|---|
| 5 | 5 * log2(26) | 23.5021 | 11.8 Million |
| 6 | 6 * log2(26) | 28.2026 | 308.9 Million |
| 7 | 7 * log2(26) | 32.9030 | 8.3 Billion |
| 8 | 8 * log2(26) | 37.6035 | 208.8 Billion |
| 12 | 12 * log2(26) | 56.4052 | 95 Quadrillion |
Using uppercase and lowercase
Use upper/lowercase, digits, & symbols
| Characters | Equation | Bits | Passwords |
|---|---|---|---|
| 5 | 5 * log2(52) | 28.5021 | 360.2 Million |
| 6 | 6 * log2(52) | 34.2026 | 19.7 Billion |
| 7 | 7 * log2(52) | 39.9030 | 1.3 Trillion |
| 8 | 8 * log2(52) | 45.6035 | 53.5 Trillion |
| 12 | 12 * log2(52) | 68.4052 | 390 Qunitrillion |
| Characters | Equation | Bits | Passwords |
|---|---|---|---|
| 5 | 5 * log2(94) | 32.7729 | 7.3 Billion |
| 6 | 6 * log2(94) | 39.3275 | 689.9 Billion |
| 7 | 7 * log2(94) | 45.8821 | 64.8 Trillion |
| 8 | 8 * log2(94) | 52.4367 | 6 Quadrillion |
| 12 | 12 * log2(94) | 78.6550 | 475 Sextillion |
So a 6 character password using at least 1 character from each possible keyboard character set, is just about as strong as a 12 character password limited to only using digits 0-9, at least from a theoretical approach.
Using digits only 0-9
Use upper/lowercase, digits, & symbols
| Characters | Equation | Bits | Passwords |
|---|---|---|---|
| 12 | 12 * log2(10) | 39.8631 | 1 Trillion |
| Characters | Equation | Bits | Passwords |
|---|---|---|---|
| 6 | 6 * log2(94) | 39.3275 | 689.9 Billion |
Dictionary attacks complicate matters
When an attacker uses a dictionary of words to try to guess your password, this can make a seemingly strong password very weak all of the sudden.
If we simply used a single all lowercase word for our password, to a human, cow might be easier to guess than supercalifragilisticexpialidocious just off the top of their head. But a computer might be doing a dictionary attack in which they would go through the total number of words in the English language (171,476 in 2020).
As we’re trying to protect against computers guessing our passwords if you figure out the entropy for these two words you’ll quickly see the pitfall of using words from any kind of dictionary in your password.
A short English word under a dictionary attack
If an attack is trying all lowercase English words to guess your password, here would be the entropy for cow:
19.9629 = 1 * log2(171,476)
Notice how we’re only using 1 character instead of what you might expect with cow having 3 characters in it? This is because if the attacker is just guessing single words, the characters in the password don’t matter at this point, if they match our single word to one in the dictionary, they’ve cracked the password.
A long English word under a dictionary attack
Now here is where things get interesting with a very long word such as supercalifragilisticexpialidocious:
19.9629 = 1 * log2(171,476)
Even though this word has 34 characters, there are only 171,476 possible combinations of all those characters to make up an English word. So we don’t gain any password entropy when a dictionary attack is being used.
A long English word under a Brute Force attack
Although if the hacker only relied on a brute force attack changing 1 character at a time, this would be an extremely strong password due to its length.
222.8560 = 34 * log2(94)
Create a strong password you can remember
Now hopefully that you understand a bit about password entropy and how to protect against automated cracking attempts of your password. This is the most common way passwords are stolen these days.
It’s also important to protect against human attacks as well, and not to leave yourself vunerable on either front. For instance while the password nowthisisastoryallabouthowmylifegotflippedturnedupsidedown would have a very high password entropy of 272.6255 with 58 characters and a possible 26 lowercase characters.
If someone knew I posted a lot about the Fresh Prince of Bel-Air and sang the intro a lot, they might suspect I’d use something silly like this as my password.
There are many methods for creating a unique strong password you can remember, but ultimately it’s going to come down to what works for you. Just be sure you know the pitfalls of not using multiple character sets or using words from any type of dictionary.
One popular method is converting a unique phrase into something you can remember with some character substitutions that only you’d think of. Here’s a simple example:
The best password is one I can remember forever
| Unique phrase | Unique character substitutions | What I did |
|---|---|---|
| The | T | Keep the capital T |
| best | b | keep the lowercase b |
| password | P | alternate back to capital P |
| is | i | keep the lowercase i |
| one | 1 | replace number one with 1 |
| I | i | back to lowercase i |
| can | C | alternate back to capital C |
| remember | r | keep the lowercase r |
| forever | 4#ver | replace for with 4, replace e with # and keep ver |
Final password
TbPi1iCr4#ver
| Characters | Equation | Bits | Passwords |
|---|---|---|---|
| 13 | 13 * log2(94) | 85.2096 | 44 Septillion |
Generate a random strong password in cPanel
If you would like to quickly generate a strong password, you can use the Change Password feature in cPanel to do so. If you wanted to actually change your cPanel password instead of just copying the password you can use it.
- Login to cPanel
- Under Administration & Help, click on Change Password.
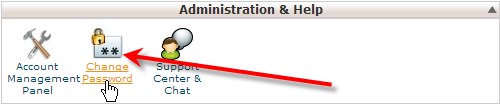
- Next click on the Password Generator button.
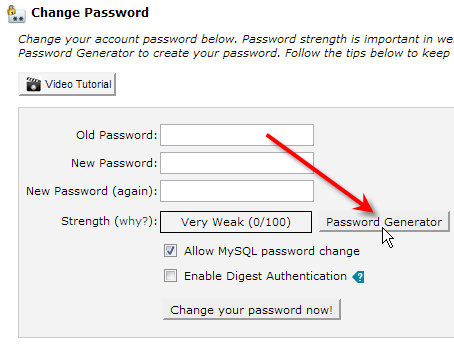
- Finally select the generated password and hit Ctrl-C to copy it.
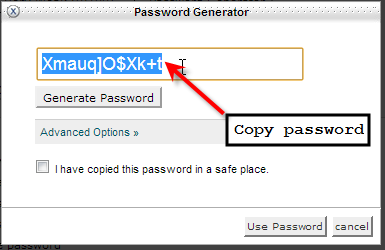
You should hopefully now have a good understanding of what it takes to create a strong secure password to keep all of your information and access secure.
Comments
It looks like this article doesn't have any comments yet - you can be the first. If you have any comments or questions, start the conversation!